Overview of Snowflake Architecture
In today’s data-driven world, organizations generate vast amounts of information every second — from customer transactions and IoT sensors to application logs and business analytics. To manage and analyze such massive data efficiently, companies rely on modern cloud data platforms. Among them, Snowflake stands out as a revolutionary cloud-based data warehouse solution built for performance, scalability, and simplicity.
The overview of Snowflake architecture helps us understand how this platform achieves remarkable speed, flexibility, and cost efficiency compared to traditional databases. Whether you’re a data professional, student, or IT enthusiast, learning Snowflake architecture opens doors to numerous career opportunities — especially if you pursue structured Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, where the demand for cloud data professionals is rapidly increasing.
Snowflake combines the best of both shared-disk and shared-nothing architectures, creating a multi-cluster, cloud-native platform that eliminates bottlenecks faced by legacy data warehouses. It’s designed to store, manage, and analyze structured and semi-structured data using SQL, while automatically handling infrastructure, scaling, and optimization in the background.
Why Understanding Snowflake Architecture Matters
Having an in-depth overview of Snowflake architecture allows professionals to grasp the underlying components that make data processing seamless and fast. It helps in:
- Building efficient data pipelines.
- Optimizing query performance.
- Reducing storage and compute costs.
- Simplifying collaboration across teams.
- Leveraging automatic scaling for real-time analytics.
In the evolving data industry, expertise in Snowflake is one of the most valuable skills — and Snowflake Training in Hyderabad offers practical learning to master these architecture principles hands-on.
Introduction to Snowflake Architecture
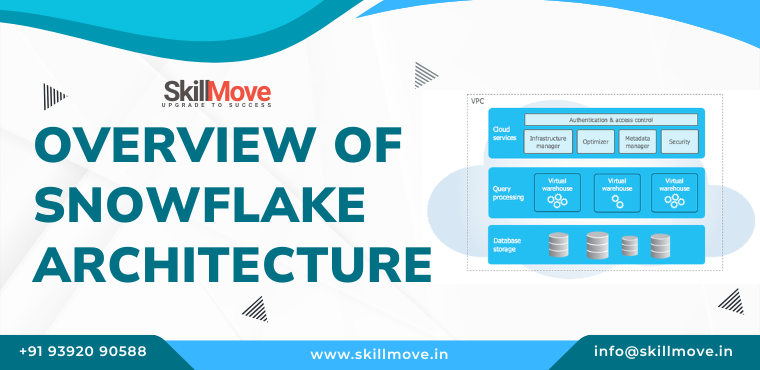
The Snowflake architecture is a fully managed cloud data warehouse designed to handle all aspects of data — storage, processing, and analysis — in one unified platform. It’s built natively for the cloud and operates entirely on public cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Unlike traditional systems that require constant hardware setup and manual tuning, Snowflake takes a service-based approach, managing everything automatically — from scaling resources to optimizing query performance. This makes it ideal for both startups and large enterprises.
At its core, the architecture is divided into three distinct yet interconnected layers:
- Database Storage Layer
- Compute Layer (Virtual Warehouses)
- Cloud Services Layer
These layers work together to provide elastic scaling, automatic optimization, and secure data sharing — the foundation of the modern Snowflake experience.
Database Storage Layer

The storage layer is where all the data lives. When data is loaded into Snowflake, it is automatically reorganized, compressed, and optimized into micro-partitions. These micro-partitions are immutable, which means once written, they are never modified — ensuring consistency and reliability.
Key Highlights:
- Data is stored in a columnar format for faster query execution.
- Snowflake automatically manages metadata and indexing, so users never have to manually optimize storage.
- Storage is separate from compute, allowing you to scale them independently.
- Data is stored securely in the cloud with AES-256 encryption by default.
For learners attending Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, mastering this storage concept is crucial to understanding how cost efficiency and performance tuning work together in Snowflake.
Compute Layer

The compute layer is the engine that performs all the data processing tasks — queries, transformations, and analytics. In Snowflake, compute resources are known as Virtual Warehouses.
Each warehouse consists of multiple compute clusters that can operate simultaneously, allowing different users or workloads to run queries independently without affecting each other.
Core Features:
Each warehouse can scale up or out automatically based on the workload.
Compute can be paused when not in use to save cost.
Dedicated compute clusters ensure no query contention between departments.
It supports multi-cluster warehouses for handling concurrent operations.
Cloud Services Layer

The Cloud Services Layer acts as the brain of the Snowflake architecture. It manages coordination, authentication, metadata, optimization, and user access.
It includes components like:
Query Parser and Optimizer: Determines the most efficient way to execute SQL queries.
Metadata Management: Tracks schema definitions, statistics, and user sessions.
Security & Governance: Implements role-based access control and encryption.
Infrastructure Management: Handles scaling, caching, and resource allocation automatically.
This layer ensures that Snowflake runs seamlessly without requiring DBA-level intervention — making it ideal for enterprises that want scalability with minimal maintenance.
The Multi-Cluster Shared Data Approach
The most innovative concept within the overview of Snowflake architecture is its multi-cluster shared data architecture.
It combines:
- Shared-disk architecture: Allows centralized data storage accessible by all compute clusters.
- Shared-nothing architecture: Provides independent compute resources, preventing query slowdowns.
This design ensures the best of both worlds — high performance and high concurrency — allowing thousands of users to query the same data simultaneously without degradation.
For students or professionals taking Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, understanding this model is essential as it forms the foundation for building enterprise-grade data solutions on Snowflake.
Advantages of Snowflake’s Architectural Design
- Separation of Compute and Storage: Scale resources independently based on workload.
- Elasticity: Automatic scaling up and down according to demand.
- Performance Optimization: Built-in caching, query optimization, and clustering.
- Concurrency: Multiple users can run queries simultaneously without delay.
- Zero Maintenance: No need to manage infrastructure manually.
- Cross-Cloud Availability: Runs on AWS, Azure, or GCP seamlessly.
Key Components of Snowflake
Understanding the key components of Snowflake is crucial to mastering how this cloud data platform achieves such exceptional performance and scalability. When you dive deeper into the overview of Snowflake architecture, you’ll notice that every element has been designed to solve long-standing data management challenges — from slow queries to storage bottlenecks and concurrency issues.
Snowflake is built on a three-layer architecture, and within those layers exist distinct components that work together seamlessly. These components are responsible for data storage, computation, query execution, security, and data management.
1. Storage Layer – The Foundation of Data
The Storage Layer is the backbone of the Snowflake architecture. This is where all raw, structured, and semi-structured data (like JSON, Parquet, and Avro) is securely stored and optimized for analytics.
When data is loaded into Snowflake, it’s automatically divided into micro-partitions, compressed, and stored in columnar format. These micro-partitions are immutable and are automatically indexed using metadata, which ensures lightning-fast query performance.
Key Highlights:
- Automatically managed and optimized data partitions.
- Stored in compressed, columnar format for efficient analytics.
- Fully encrypted using AES-256 encryption both at rest and in transit.
- Separation from compute ensures flexible and independent scaling.
For example, if a business stores customer transaction data, Snowflake ensures that only the required partitions are scanned during queries, saving both time and cost.
In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners get hands-on practice loading, transforming, and managing data inside this storage layer, understanding how micro-partitions improve performance and reduce query latency.
2. Compute Layer – Virtual Warehouses
The Compute Layer, often referred to as Virtual Warehouses, is where all data processing happens — querying, transforming, aggregating, and loading.
Snowflake allows multiple virtual warehouses to run simultaneously, each dedicated to different workloads or teams. This design prevents resource contention, meaning marketing teams, analysts, and developers can all work on the same dataset without slowing each other down.
Core Features of the Compute Layer:
- Independent scaling for each warehouse (scale up for power, scale out for concurrency).
- Automatic suspension and resumption for cost efficiency.
- Multi-cluster support for handling thousands of concurrent queries.
Instant spin-up and shutdown with no warm-up time.
Example:
Imagine your company’s finance department is generating monthly reports while your AI team is running machine learning models — both can work at full speed without waiting for resources, thanks to Snowflake’s independent virtual warehouse concept.
This elastic compute capability is a key reason why Snowflake Training in Hyderabad focuses heavily on virtual warehouse configuration, performance tuning, and workload optimization.
3. Cloud Services Layer – The Control System
The Cloud Services Layer acts as the central control unit of Snowflake architecture. It manages system metadata, authentication, optimization, and access control.
It’s what makes Snowflake serverless — meaning users don’t need to manage clusters, nodes, or hardware manually. Everything from query optimization to scaling is handled by Snowflake’s internal algorithms.
Main Components of the Cloud Services Layer:
- Query Parser & Optimizer: Analyzes incoming SQL queries and determines the most efficient execution plan.
- Metadata Manager: Tracks objects like databases, schemas, tables, and query statistics.
- Security Manager: Enforces role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring only authorized users can access data.
- Infrastructure Manager: Allocates compute and manages auto-scaling dynamically.
- Transaction Manager: Maintains data consistency and concurrency.
This layer is what truly differentiates Snowflake from manual database systems. It automates the heavy lifting, allowing data engineers and analysts to focus on insights rather than infrastructure.
4. Metadata Repository – The Smart Index
A unique aspect of the Snowflake architecture overview is how efficiently it manages metadata, which drives performance, recovery, and cost optimization.
Snowflake automatically gathers metadata for every table, schema, and query — including details like storage size, distribution, and query statistics. This automation ensures continuous optimization without manual tuning. The metadata is then used to:
- Optimize future queries using caching and pruning.
- Track historical performance for better analytics.
- Enable Time Travel and Fail-safe recovery to restore deleted or modified data.
The Time Travel feature lets users access previous versions of data for up to 90 days, depending on the plan. Combined with Fail-safe, it ensures reliable data recovery even after critical errors.
For learners pursuing Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, understanding metadata management is vital. It helps in cost control, faster query execution, and seamless data recovery, all of which are key to real-world data engineering and analytics operations.
5. Data Sharing Component – Secure Collaboration
One of Snowflake’s most revolutionary features is its Secure Data Sharing capability, which allows organizations and departments to share live, ready-to-query data instantly without copying, moving, or exporting it.
For example, a retail company can securely share real-time sales data with suppliers, logistics partners, or analytics teams — all without creating duplicate files or increasing storage costs. The data stays in the provider’s account but becomes immediately queryable to the recipient through Snowflake’s secure infrastructure.This feature is powered by Snowflake’s multi-cluster, shared-data architecture, ensuring that data sharing is instant, cost-efficient, and fully governed.
Key Benefits:
- No data duplication or transfer costs.
- Real-time visibility and synchronization.
- Enterprise-grade security and compliance.
- Improved collaboration between business units and partners.
For learners enrolled in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, mastering Secure Data Sharing is vital to understanding real-world enterprise collaboration, access control, and data governance in modern cloud ecosystems.
6. Query Processing Engine – The Performance Core
At the heart of Snowflake’s compute layer lies its query processing engine, which executes user queries using a combination of distributed computing and optimization.
When a query is executed, Snowflake’s optimizer determines the most efficient plan, leveraging caching, partition pruning, and parallel processing.
Performance Features:
- Result Caching: Reuses previous query results to avoid re-computation.
- Metadata Caching: Speeds up repeated query execution.
- Pruning & Clustering: Ensures only relevant data partitions are scanned.
- Query Acceleration: Uses vectorized execution and optimized I/O.
These features combine to provide lightning-fast query performance — one of the biggest advantages highlighted in every overview of Snowflake architecture.
Professionals who complete Snowflake Training in Hyderabad gain direct experience writing and optimizing queries using these advanced features, giving them an edge in analytics and data engineering roles.
7. Security and Compliance Layer
Security is built into every layer of Snowflake. From encryption to access control, the platform ensures enterprise-grade protection for sensitive data.
Security Components Include:
- End-to-End Encryption (AES-256): Protects data both at rest and in motion.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds extra user security.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Restricts data access to authorized users.
- Automatic Key Rotation: Ensures ongoing encryption security.
- Compliance Certifications: Snowflake complies with GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 standards.
This strong security framework makes Snowflake ideal for industries like finance, healthcare, and retail, where data privacy and compliance are non-negotiable.
Through Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, participants learn to implement these controls, configure roles, and manage secure data sharing environments.
8. Connectivity and Integration Layer
The connectivity layer in Snowflake is one of its strongest advantages, enabling seamless integration with a wide range of external tools and platforms across the data ecosystem.
Snowflake supports connectivity with:
- ETL tools such as Talend, Informatica, and Apache NiFi for smooth data extraction, transformation, and loading.
- Business Intelligence (BI) tools like Power BI, Tableau, and Looker for advanced visualization and reporting.
- Machine Learning platforms including Python, R, Databricks, and AWS SageMaker for predictive modeling and AI-driven analytics.
- Data Integration APIs through REST, ODBC, JDBC, and SnowSQL, allowing developers to build custom applications and automated workflows.
This flexible ecosystem enables organizations to build end-to-end data pipelines, with Snowflake as the core hub for storage, processing, and analytics. It ensures scalability and seamless collaboration across teams.
For learners taking Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, understanding these integrations helps them connect Snowflake with ETL, BI, and ML tools, creating efficient, real-world data workflows for modern enterprises.
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Layer | Stores and optimizes data | Micro-partitioned storage |
| Compute Layer | Executes data processing | Virtual Warehouses |
| Cloud Services Layer | Manages and optimizes operations | Query optimization |
| Metadata Repository | Tracks schema and query info | Time Travel |
| Data Sharing | Enables collaboration | Secure data sharing |
| Query Engine | Executes optimized queries | Result caching |
| Security Layer | Ensures protection and compliance | AES-256 encryption |
| Integration Layer | Connects to external tools | Power BI, Python, APIs |
In summary, each of these key components of Snowflake works harmoniously to deliver a powerful, flexible, and secure cloud data warehouse.
The more you understand these components, the better you can build optimized data solutions — which is why mastering them through Snowflake Training in Hyderabad is essential for anyone aiming to advance in cloud data engineering or analytics.
How Snowflake Differentiates from Traditional Databases
A clear overview of Snowflake architecture isn’t complete without understanding how it breaks away from the limitations of on-premise and legacy database systems. For decades, relational databases like Oracle, SQL Server, or Teradata dominated the analytics landscape. They worked well for structured, predictable workloads—but today’s businesses generate massive, fast-changing, and semi-structured data that demand elasticity and real-time analytics.
That’s where Snowflake comes in—a born-in-the-cloud data platform designed to handle modern data challenges.
Below are the key differences that make Snowflake a preferred choice for enterprises and professionals pursuing Snowflake Training in Hyderabad to stay industry-ready.
1. Cloud-Native vs On-Premise Infrastructure
Traditional databases run on physical servers or virtual machines managed by IT teams. Scaling requires adding new hardware, taking downtime, and high upfront investment.
Snowflake, in contrast, is fully cloud-native. It runs seamlessly on AWS, Azure, and GCP, scaling automatically based on workload demand. No hardware, no installations, and no manual upgrades.
| Feature | Traditional Databases | Snowflake |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | On-prem / self-hosted | Fully managed in cloud |
| Scaling | Manual, hardware-based | Auto-scaling in seconds |
| Maintenance | DBA-driven | Vendor-managed |
| Cost Model | Fixed CapEx | Pay-as-you-use OpEx |
For learners, Snowflake Training in Hyderabad teaches how to deploy and scale cloud-based warehouses instantly—something that’s impossible in legacy systems.
2. Separation of Compute and Storage
One of the biggest architectural innovations highlighted in any overview of Snowflake architecture is the complete separation of compute and storage.
Traditional databases couple compute and storage together—when storage grows, compute power must also grow, leading to waste and inefficiency.
Snowflake decouples them:
- Storage scales for large datasets.
- Compute (virtual warehouses) scales independently for workload concurrency.
This independence means you can run dozens of simultaneous queries without performance drops.
Example: Marketing, Finance, and AI teams can each use separate warehouses on the same data—no blocking, no waiting.
This design drastically reduces cost, making Snowflake attractive for enterprises and a critical concept in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad modules.
3. Elasticity and Auto-Scaling
Legacy databases require DBAs to predict capacity in advance. If usage spikes, systems slow down; if demand drops, expensive hardware sits idle.
Snowflake’s multi-cluster elastic architecture automatically adds or removes compute clusters based on load. It even suspends idle warehouses to save cost.
This elasticity supports unlimited concurrency, ideal for organizations with fluctuating workloads—such as retail during festive seasons or financial reporting at month-end.
In practice sessions during Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, students learn how to monitor warehouses, view auto-scaling in real time, and optimize billing.
4. Data Sharing Without Data Movement
Traditional databases rely on file exports (CSV, JSON) and manual transfers to share data, which leads to duplication, version mismatches, and security risks.
Snowflake introduces Secure Data Sharing—allowing instant, live data access between departments or partners without copying or moving data.
Benefits:
- Zero duplication and transfer cost.
- Real-time insights for all users.
- Centralized governance and version control.
This capability redefines collaboration in enterprises and is a major topic covered in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, where learners simulate real-world partner data exchanges.
5. Support for Semi-Structured and Unstructured Data
Traditional relational systems excel at structured data (tables, rows, columns) but struggle with JSON, Parquet, or Avro formats.
Snowflake natively supports semi-structured and unstructured data using its VARIANT data type and Snowpark functions. Developers can run SQL queries directly on JSON without complex ETL conversions.
Example:
SELECT user_data:name, user_data:email FROM customer_json;
Snowflake automatically parses and flattens JSON keys during query execution. This flexibility is vital for data scientists, making Snowflake Training in Hyderabad a popular choice among analytics aspirants transitioning from traditional SQL environments.
6. Performance Optimization and Caching
Legacy databases depend heavily on manual indexing and tuning by DBAs.
Snowflake, however, uses automatic optimization and intelligent caching:
- Result Caching: Reuses previous query results for identical requests.
- Metadata Caching: Stores table and partition stats.
- Micro-partition Pruning: Reads only necessary partitions.
This built-in intelligence ensures consistent sub-second performance for repetitive workloads, even with terabytes of data.
In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, you’ll learn how to analyze query plans, leverage caching, and minimize compute credits for maximum efficiency.
7. Security, Governance & Compliance
Traditional databases require separate add-ons for encryption, key management, and auditing.
Snowflake integrates security at every layer:
- End-to-end encryption (AES-256).
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
- Multi-factor authentication and SSO.
- Data masking and row-level security.
- Industry compliance: GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2 Type II.
This simplifies governance while maintaining enterprise-grade protection. Professionals trained in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad gain practical experience setting up secure roles, warehouses, and masked views for sensitive data.
8. Maintenance and Administration
Legacy databases demand constant patching, backups, and indexing—consuming valuable DBA hours.
Snowflake’s zero-maintenance model automates all of it:
- Automatic backups and disaster recovery.
- Instant cloning for test environments.
- Auto-vacuuming of unused space.
- Continuous upgrades without downtime.
This frees IT teams to focus on strategic analytics rather than routine maintenance.
During Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners see this in action—creating clones, restoring tables via Time Travel, and viewing Snowflake’s fail-safe mechanism.
9. Cost Efficiency and Usage Model
Traditional data warehouses operate on fixed licensing and hardware costs.
Snowflake adopts a pay-per-second consumption model, allowing organizations to pay only for compute and storage they actually use.
Example: If a warehouse runs for 5 minutes, you’re billed only for those 300 seconds.
Combined with auto-suspend features, Snowflake provides unmatched cost control—another highlight frequently discussed in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad courses for budget optimization.
10. Cross-Cloud and Multi-Region Support
Traditional databases are limited to a single environment or data center.
Snowflake’s multi-cloud and multi-region architecture allows enterprises to deploy and replicate data across AWS, Azure, and GCP instantly, ensuring high availability and disaster recovery.
Organizations can even share data securely across cloud providers—an essential feature for global companies.
This cross-platform compatibility is one reason Snowflake architects are in high demand; thus, Snowflake Training in Hyderabad programs emphasize cross-cloud replication and failover labs.
| Feature | Traditional | Snowflake |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | On-prem / VM | Cloud-native SaaS |
| Scaling | Manual | Auto-elastic |
| Storage | Coupled with compute | Fully separated |
| Maintenance | Manual | Automatic |
| Data Types | Structured only | Structured + Semi-structured |
| Concurrency | Limited | Virtually unlimited |
| Cost | Fixed | Pay-as-you-go |
| Data Sharing | File-based | Live Secure Share |
| Security | Add-on modules | Built-in governance |
Why These Differences Matter
The architectural innovations explained in this overview of Snowflake architecture aren’t just theoretical—they deliver tangible business results:
- Faster decision-making with instant scalability.
- Lower infrastructure costs through consumption-based billing.
- Improved collaboration via secure data sharing.
- Simplified management through automation.
- Cross-cloud freedom for hybrid enterprises.
These are the reasons thousands of engineers and analysts are enrolling in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, equipping themselves with the skills to design next-generation cloud data solutions.
Data Storage in Snowflake
When exploring the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, one of the most essential layers to master is data storage. Snowflake completely re-imagines how enterprise data is organized, compressed, and retrieved in the cloud. Unlike legacy warehouses that depend on rigid file systems or disks, Snowflake’s storage layer provides virtually unlimited capacity, automatic optimization, and seamless scaling without any manual administration.
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture reveals that Snowflake separates storage from compute. This single innovation enables flexible cost management, improved concurrency, and on-demand performance.
Learners enrolled in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad spend significant time working with this storage layer, learning how data is partitioned, encrypted, and optimized for analytics.
1. Columnar Data Organization
At the heart of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture lies its columnar storage model. Data is stored column-wise rather than row-wise, which allows Snowflake to read only the columns relevant to a query. This drastically reduces I/O, improving query response times.
Benefits of columnar architecture:
- Efficient data compression through similarity in column values.
- Faster analytical processing on large datasets.
- Reduced compute usage, translating to lower costs.
- Ideal for aggregate and OLAP queries common in business analytics.
In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, students learn how columnar storage improves performance using sample sales and IoT datasets.
2. Micro-Partitioning — The Core Storage Technique
A detailed Overview of Snowflake Architecture always includes the concept of micro-partitioning. Snowflake automatically divides data into small, contiguous units called micro-partitions (each about 50–500 MB compressed).
These micro-partitions:
- Store metadata about data ranges (like min/max values).
- Enable partition pruning, scanning only relevant partitions during queries.
- Are immutable — once written, they’re never updated, ensuring data integrity.
This automatic design means no manual partition management, indexes, or vacuuming as in traditional systems.
Professionals mastering Snowflake through Snowflake Training in Hyderabad quickly understand how micro-partition pruning directly impacts query cost and speed—key to real-world optimization.
3. Secure and Encrypted Storage
Security is embedded into every level of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, especially within storage. All data is encrypted using AES-256 encryption both at rest and in transit. Encryption keys rotate automatically, ensuring maximum protection.
Key Security Highlights:
- End-to-end encryption with automatic key management.
- Multi-layer encryption hierarchy (root keys → database keys → file keys).
- Support for Customer-Managed Keys (CMK) in Enterprise editions.
- Storage complies with SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and HIPAA standards.
Learners in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad are guided through practical labs on data masking and secure data sharing—two topics deeply connected to Snowflake’s encrypted storage system.
4. Automatic Compression and Optimization
Another vital aspect of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is its built-in data compression engine. Snowflake automatically chooses the most efficient compression algorithm for each column based on its content.
This means you get maximum performance and minimum storage cost without doing anything manually.
Example:
Numeric columns use run-length encoding; textual columns use dictionary encoding.
On average, data compressed in Snowflake uses up to 80% less space than raw storage.
When students practice labs during Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, they observe how automatic compression impacts credit usage and billing—turning the theory behind the Overview of Snowflake Architecture into practical insight.
5. Metadata and Data Cataloging
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture also emphasizes metadata management as a core strength. Snowflake automatically tracks every object — tables, views, columns, micro-partitions, and query statistics.
This metadata is stored in Snowflake’s central cloud services layer and powers:
- Query Optimization via automatic statistics.
- Time Travel and Fail-Safe for data recovery.
- Data Governance through lineage tracking and auditing.
Metadata is fully managed by Snowflake — no manual indexing or stats collection required.
Students in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad learn how metadata enhances query execution plans and simplifies data governance compliance.
6. Time Travel and Fail-Safe Mechanisms
A unique feature within the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is Time Travel — allowing users to access historical data versions for a specified period (1 to 90 days depending on edition).
If data is accidentally deleted or modified, you can restore it using a simple SQL command:
SELECT * FROM sales_table AT (OFFSET => -86400);
The Fail-Safe feature retains data for 7 additional days after Time Travel expires, ensuring full disaster recovery.
This protection layer demonstrates why the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is considered the most resilient design among modern data warehouses.
During hands-on sessions in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, students simulate accidental deletes and restore data using Time Travel queries — a critical enterprise skill.
7. Separation of Storage and Compute Revisited
While discussing data storage, the Overview of Snowflake Architecture must highlight how compute resources (virtual warehouses) operate independently of the storage layer.
Benefits:
- Storage grows linearly with data volume without impacting compute costs.
- Multiple teams query the same data without performance loss.
- Warehouses can be paused or resumed without affecting data availability.
This separation is a cornerstone of Snowflake’s elastic architecture and a major focus area in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad for architects and data engineers.
8. Smart Clustering and Partition Pruning
Another innovation within the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is Automatic Clustering. Traditional systems require manual index creation; Snowflake continuously monitors micro-partition metadata and adjusts clustering as data grows.
Clustering keys can be defined manually for specific performance needs, but in most cases Snowflake handles this automatically.
This leads to faster queries on large fact tables like sales, logs, or IoT streams.
In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners practice defining clustering keys and measuring performance gains through the SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_INFORMATION() function.
9. Storage Cost Management
From a financial perspective, the Overview of Snowflake Architecture also teaches that storage costs are billed separately from compute usage.
Cost Optimization Tips:
- Compress data before loading.
- Use automatic data retention policies.
- Archive rarely used tables to lower-cost storage.
- Monitor storage usage through Account Usage views.
Professionals trained in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad learn how to analyze these costs using SQL and Snowflake’s built-in dashboard.
Summary of Data Storage in the Overview of Snowflake Architecture
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Columnar Storage | Stores data column-wise | Fast analytics performance |
| Micro-Partitioning | Automatic data segmentation | Efficient pruning and query speed |
| Encryption | AES-256 end-to-end | Maximum data security |
| Time Travel & Fail-Safe | Restore past data versions | Disaster recovery |
| Compression | Automatic per column | Lower storage cost |
| Metadata Management | Tracks all objects and stats | Query optimization |
| Separation of Storage & Compute | Independent scaling | Flexibility & cost control |
Compute Resources in Snowflake
A complete Overview of Snowflake Architecture would be incomplete without understanding its most dynamic engine — the compute resources. While the storage layer safeguards and organizes data, it’s the compute layer that actually performs queries, transformations, and analytics.
In the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, compute resources are known as Virtual Warehouses. These are isolated, elastic clusters of compute power that execute all SQL statements. Every data-driven organization relies on these compute engines for daily dashboards, ETL jobs, and AI pipelines.
Learners enrolled in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad spend significant hands-on time configuring, scaling, and monitoring these warehouses — one of the most critical skills for Snowflake developers and architects.
1. What Is a Virtual Warehouse?
Within the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, a Virtual Warehouse is a compute cluster made up of one or more nodes running in the cloud. Each node contains CPU, memory, and temporary storage used for query processing.
Whenever a user executes a query, a warehouse spins up, processes the task, and returns the result without interfering with other workloads.
Key Points:
- Each warehouse is independent and can be paused or resumed instantly.
- Warehouses don’t store data themselves; they read from the central storage layer.
- They can be sized (S–4XL) depending on performance needs.
- Multiple warehouses can run queries on the same data concurrently without conflict.
This level of flexibility is a key reason why the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is a paradigm shift from traditional databases. Students in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad gain practical experience configuring these warehouses for ETL, BI, and ad-hoc queries.
2. How Compute Interacts with Storage
A central principle of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is that compute and storage are fully decoupled. When a warehouse runs a query, it retrieves data from the centralized storage layer, processes it in memory, and writes the results back to storage.
This means you can scale compute up or down without affecting stored data. It’s especially useful for enterprises with fluctuating data workloads.
In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners experiment with various warehouse sizes and observe how they affect query speed and credit consumption, building a realistic understanding of cost optimization within the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
3. Scaling Compute Resources
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture emphasizes two types of scaling within compute resources:
- Vertical Scaling (Scale Up): Increasing the size of a single warehouse from Small to Medium to Large to XLarge for heavier workloads.
- Horizontal Scaling (Scale Out): Adding multiple clusters of the same size in a multi-cluster warehouse for high concurrency.
Example: If hundreds of analysts run queries at once, Snowflake automatically adds clusters to avoid slowdowns, then shuts them off when idle.
This elastic scaling ensures optimal performance and is a core topic in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, where students simulate multi-user workloads and analyze resource utilization metrics.
4. Auto-Suspend and Auto-Resume
A key innovation in the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is auto-suspend and auto-resume features.
- Auto-Suspend: If a warehouse remains idle for a set period (say 5 minutes), it pauses automatically to save credits.
- Auto-Resume: When a new query arrives, the warehouse resumes instantly within seconds.
This feature ensures organizations only pay for compute when it’s actually used — a key factor highlighted in every practical Overview of Snowflake Architecture discussion.
Professionals in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad use these features to build cost-optimized pipelines and monitor credit usage across teams.
5. Query Optimization and Performance
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture details an advanced query optimizer embedded within the Cloud Services Layer. This optimizer analyzes SQL statements, metadata, and statistics to generate the most efficient execution plan.
Optimization Techniques:
- Automatic Caching: Stores frequently used query results.
- Pruning: Reads only relevant micro-partitions.
- Vectorized Execution: Processes multiple data points simultaneously.
- Result Reuse: Avoids redundant computation across sessions.
In hands-on labs within Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, students learn to read query profiles, interpret execution graphs, and use SQL functions like SYSTEM$QUERY_HISTORY() to evaluate performance within the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
6. Workload Isolation and Concurrency
Traditional databases often suffer from “noisy neighbor” issues where one heavy query slows down others.
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture solves this with workload isolation. Each virtual warehouse operates independently, meaning ETL jobs, reporting, and data science tasks run in parallel without contention.
Example: Finance queries run on Warehouse-A while Marketing dashboards run on Warehouse-B — both read the same central data but don’t interfere with each other.
This design makes the Overview of Snowflake Architecture ideal for large organizations with multiple teams. During Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, students build multi-warehouse setups to see isolation and scaling in action.
7. Multi-Cluster Warehouses for Concurrency
When dozens or hundreds of queries run simultaneously, multi-cluster warehouses automatically add more clusters to handle demand. This is a defining feature in the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
Key Advantages:
- Eliminates query queueing or timeouts.
- Dynamically adapts to user load.
- Ensures consistent response times for critical dashboards.
In enterprise projects built during Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, participants configure multi-cluster warehouses and analyze credit consumption patterns — essential for cost-performance trade-off mastery.
8. Monitoring and Resource Management
Every Overview of Snowflake Architecture discussion must include monitoring tools that keep compute usage transparent and efficient.
Snowflake offers built-in views like WAREHOUSE_LOAD_HISTORY and QUERY_HISTORY, enabling administrators to track query duration, credit usage, and performance bottlenecks.
Through Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, students learn to visualize these metrics inside the web UI and integrate them with BI dashboards like Tableau and Power BI to build custom monitoring systems for real-time visibility into the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
9. Cost Optimization Strategies
Since compute is billed per second, managing credits wisely is vital.
Best Practices Derived from the Overview of Snowflake Architecture:
- Use smaller warehouses for light queries.
- Set auto-suspend to 2 or 3 minutes for idle time.
- Create separate warehouses for different departments to track cost accurately.
- Monitor usage via Account Usage views or Snowflake billing API.
Real-world projects during Snowflake Training in Hyderabad teach these cost optimization tactics, turning learners into practically skilled architects who understand the financial side of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
10. Compute Resources Summary
| Aspect | Traditional Databases | Snowflake (Overview of Snowflake Architecture) |
|---|---|---|
| Compute Scaling | Manual hardware upgrade | Automatic vertical and horizontal scaling |
| Concurrency | Limited | Unlimited via multi-cluster warehouses |
| Maintenance | DBA-dependent | Zero maintenance |
| Cost Model | Fixed licensing | Pay-as-you-use |
| Performance | Index and tuning needed | Auto-optimized with caching |
| Isolation | Shared resources | Independent warehouses |
Benefits of Snowflake Architecture
When examining the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, one quickly realizes why Snowflake has become the dominant force in modern data warehousing. Its architecture offers an intelligent combination of scalability, security, performance, and simplicity — all built for the cloud.
Organizations that migrate to Snowflake often experience drastic improvements in query performance, maintenance efficiency, and cost reduction. For learners pursuing Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, understanding these benefits not only deepens technical comprehension but also demonstrates how architectural design directly drives business value.
1. Elastic Scalability
A major benefit highlighted throughout the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is elastic scalability. Traditional databases require manual provisioning of servers or nodes. Snowflake, being cloud-native, automatically scales compute and storage based on workload demands.
Key Advantages of Elastic Scaling:
- Scale up for large batch jobs or machine learning training.
- Scale out to handle hundreds of concurrent queries.
- Pause warehouses to save cost during low activity.
This on-demand elasticity ensures consistent performance and predictable costs — one of the most practical lessons demonstrated in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad through live workload simulations.
2. High Performance and Query Optimization
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture shows how Snowflake’s built-in optimizer, result caching, and micro-partition pruning create an ecosystem of speed.
Performance Highlights:
- Sub-second response times on billions of rows.
- Automatic query optimization without index management.
- Smart metadata caching reduces I/O load.
For businesses, this means instant insights and faster decisions. In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners observe real-world performance gains by comparing query execution plans across different warehouse sizes.
3. Cost Efficiency and Pay-As-You-Use Model
Another major strength discussed in the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is its flexible pay-per-use pricing. Compute and storage are decoupled, so companies pay only for what they use — not for idle resources.
Cost Benefits:
- Pause warehouses during idle hours to stop billing.
- Choose warehouse sizes based on real-time needs.
- Storage is inexpensive and compressed automatically.
These financial efficiencies are crucial topics in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, where learners learn to interpret account usage reports and apply cost-control best practices within the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
4. True Workload Isolation
One of the most revolutionary ideas in the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is workload isolation through independent virtual warehouses.
Each warehouse processes queries separately, ensuring one team’s activity doesn’t impact another’s performance.
Example: Data engineering teams can run heavy ETL loads while data scientists analyze models — without bottlenecks.
This separation allows different teams, departments, or even external partners to work in parallel with no degradation of performance. It’s a real-world scenario covered extensively in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad lab sessions.
5. Built-In Security and Compliance
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture integrates security into every layer — storage, compute, and cloud services.
Security Mechanisms:
- End-to-end AES-256 encryption for data in transit and at rest.
- Multi-factor authentication and SSO.
- Role-based access control (RBAC).
- Automatic key rotation and tokenization.
- Certifications including GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 Type II.
These features make Snowflake ideal for industries like finance and healthcare. In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners simulate compliance scenarios by configuring roles, policies, and masked views — turning theory from the Overview of Snowflake Architecture into applied skill.
6. Zero Maintenance and Automation
A defining aspect of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is that Snowflake handles all system maintenance automatically — no indexing, vacuuming, or patching required.
Automation Benefits:
- Automatic query tuning and optimization.
- Built-in backups and disaster recovery via Fail-Safe.
- Continuous system updates without downtime.
This “hands-free” architecture allows engineers to focus on insights instead of infrastructure. It’s one of the top reasons cited by enterprises migrating to Snowflake, and a concept demonstrated in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad through automated pipeline management exercises.
7. Multi-Cloud Flexibility
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture was designed to be cloud-agnostic from day one. It runs seamlessly on AWS, Azure, and GCP, allowing organizations to choose their preferred provider — or operate across several simultaneously.
Advantages of Multi-Cloud Deployment:
- Avoids vendor lock-in.
- Improves disaster recovery capabilities.
- Enables cross-region data replication and sharing.
Professionals trained through Snowflake Training in Hyderabad learn how to configure multi-region accounts and manage cross-cloud data replication as part of advanced modules within the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
8. Seamless Data Sharing and Collaboration
Snowflake’s Secure Data Sharing capability — one of the crown jewels of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture — lets organizations share live, query-ready data instantly without duplication or transfers.
Business Benefits:
- Faster partnership analytics without ETL steps.
- Real-time collaboration across departments or vendors.
- Enhanced data governance and trust.
Learners in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad build secure data-sharing demos between mock organizations to master this real-world feature.
9. Support for Diverse Data Types and Workloads
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture shows Snowflake’s ability to handle structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data with equal efficiency.
Examples:
- Structured data: Customer transactions in tables.
- Semi-structured: JSON from web apps and IoT devices.
- Unstructured: Images or PDFs stored in Snowflake stages.
Snowflake unifies these formats under a single SQL interface, eliminating the need for separate systems. This multi-format capability is a key module in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, helping learners build modern data lakes on top of the core Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
10. Business Continuity and Reliability
Finally, the Overview of Snowflake Architecture ensures 99.9% uptime SLA and continuous availability through redundancy and replication across zones.
Reliability Features:
- Automatic failover between regions.
- Time Travel and Fail-Safe for data restoration.
- Cloud Service resiliency layer for query coordination.
This reliability gives businesses confidence that their data environment will stay operational under any circumstance. In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, students perform failover exercises and simulate multi-region restoration scenarios to appreciate the stability built into the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
Summary of Benefits in the Overview of Snowflake Architecture
| Category | Traditional Systems | Snowflake (Cloud-Native Architecture) |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Manual hardware | Automatic elastic scaling |
| Performance | Index and tuning required | Built-in optimizer & caching |
| Cost Model | Fixed licensing | Pay-as-you-use |
| Security | Add-on tools | End-to-end encryption & RBAC |
| Maintenance | High overhead | Zero maintenance |
| Collaboration | File exports | Secure live sharing |
| Cloud Support | Single environment | Multi-cloud deployment |
Real-World Use Cases of Snowflake Architecture
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture isn’t just theory — it’s an enterprise-ready system already transforming how organizations store, process, and share data.
Below are the five most practical examples of how leading industries apply Snowflake’s unique architecture to achieve real-time insights, scalability, and security.
Students who pursue Snowflake Training in Hyderabad often work on these same domains to gain project-based, hands-on experience.
1. Finance & Banking — Risk Analytics and Regulatory Reporting
Financial institutions deal with billions of transactions daily, demanding reliability and compliance.
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture enables:
- Elastic scaling for peak trading hours.
- Secure data sharing with regulators without file exports.
- Data masking and role-based access control for privacy.
- Real-time fraud detection using multi-cluster warehouses.
Banks now generate risk dashboards in minutes rather than hours.
In Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners simulate these environments, creating compliance-ready analytics pipelines on top of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
2. Healthcare & Life Sciences — Data Interoperability and Compliance
Hospitals and pharma companies rely on the Overview of Snowflake Architecture to unify patient records and research data securely.
How Snowflake helps:
- End-to-end AES-256 encryption meets HIPAA standards.
- Time Travel preserves historical versions of clinical data.
- Secure Data Sharing connects multiple hospitals without duplication.
- JSON support stores unstructured lab reports and device logs.
This capability reduces integration time for clinical studies by up to 70%.
Students in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad learn to implement governed data pipelines that mirror these real-world healthcare use cases within the Overview of Snowflake Architecture.
3. Retail & E-Commerce — Customer 360° and Inventory Insights
Retailers use the Overview of Snowflake Architecture to build a single source of truth for sales, inventory, and customer behavior.
Key Outcomes:
- Centralized storage for online and in-store transactions.
- Semi-structured support (JSON) for clickstream and social data.
- Predictive analytics for inventory and demand forecasting.
- Integration with BI tools like Tableau and Power BI.
This results in personalized marketing and reduced stockouts.
During Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners build Customer 360 dashboards using live datasets to see the Overview of Snowflake Architecture in action.
4. Manufacturing & IoT — Predictive Maintenance
Factories generate continuous machine sensor data that traditional systems cannot analyze in real time.
Using the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, manufacturers achieve:
- Micro-partitioned storage for millions of IoT signals.
- Streaming analytics for machine performance.
- Integration with ML tools for predictive maintenance.
- Centralized dashboards for operations and quality control.
These solutions reduce equipment downtime and boost productivity.
Hands-on projects in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad teach students how to use the compute-storage separation from the Overview of Snowflake Architecture to analyze IoT data streams.
5. Media & Entertainment — Audience Engagement and Ad Analytics
Streaming platforms apply the Overview of Snowflake Architecture to process massive user-behavior and advertising data in real time.
Advantages:
- Multi-cluster warehouses ensure smooth analytics during peak traffic.
- Semi-structured support for JSON view logs.
- Secure sharing of audience segments with ad partners.
- Fast content performance reporting for marketing teams.
Media companies improve personalization accuracy and ad ROI significantly.
Through Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners replicate these ad analytics pipelines, observing how the Overview of Snowflake Architecture delivers speed and scale for data-heavy industries.
Use Cases in the Overview of Snowflake Architecture
| Industry | Use Case | Core Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Risk & Fraud Detection | Elastic scaling and compliance |
| Healthcare | Clinical Data Exchange | HIPAA security + governed sharing |
| Retail | Customer 360 Insights | Unified view + predictive analytics |
| Manufacturing | Predictive Maintenance | IoT data scalability |
| Media | Ad & Audience Analytics | Real-time performance tracking |
Future Scope and Learning Snowflake
- The Overview of Snowflake Architecture is not just a framework for understanding how modern data systems work—it’s a roadmap for the future of cloud data engineering. As organizations across industries move away from legacy on-premise data warehouses toward scalable cloud solutions, Snowflake has positioned itself as the industry leader in performance, automation, and cross-cloud integration. In today’s digital landscape, where businesses require platforms that are fast, secure, and intelligent, the Overview of Snowflake Architecture delivers unmatched flexibility through its separation of compute, storage, and services. This innovation has made Snowflake one of the most in-demand technologies in 2025 and beyond. For learners and professionals pursuing Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, mastering this architecture provides both technical mastery and strategic insight to design, implement, and optimize end-to-end data solutions at an enterprise level.
- Across sectors like finance, retail, healthcare, and AI, companies are increasingly adopting Snowflake because it offers multi-cloud flexibility on AWS, Azure, and GCP; zero-maintenance automation; secure live data sharing; and built-in scalability for real-time analytics. As highlighted in every layer of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, this cloud-first design eliminates infrastructure bottlenecks and manual tuning, making Snowflake experts highly valuable in the job market. Recent surveys show that Snowflake developers, architects, and data engineers earn some of the highest salaries in data and cloud careers, which is why structured Snowflake Training in Hyderabad is considered a smart career investment for those entering or transitioning into data analytics, engineering, or cloud computing roles.
- Understanding the Overview of Snowflake Architecture is the foundation, but true expertise lies in mastering the full ecosystem around it. Learners in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad develop core skills such as building and managing Virtual Warehouses for performance optimization, implementing advanced features like Time Travel, Fail-Safe, and Secure Data Sharing, and integrating Snowflake with BI, ETL, and AI tools such as Power BI, Talend, and Python. They also learn to secure data using RBAC, manage encryption policies, monitor performance, and optimize cost through real-time credit management. These capabilities prepare students for job roles such as Snowflake Data Engineer, Cloud Architect, BI Developer, and Data Analyst, all of which are seeing exponential global demand.
- The future scope outlined in the Overview of Snowflake Architecture demonstrates that Snowflake is far more than a data warehouse—it is a continuously evolving Data Cloud Ecosystem. Unlike traditional systems, Snowflake is expanding its integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning workflows, offering advanced tools like Snowpark for Python, MLflow integration, and real-time data streaming for near-instant analytics. Future updates will enhance cost governance, automate scaling even further, and introduce unstructured and vector data support to serve GenAI and LLM-based models. Because of this, Snowflake Training in Hyderabad is not only relevant for developers but also essential for data scientists, BI professionals, and cloud architects who wish to future-proof their skills and stay competitive in the rapidly evolving data industry.
- To effectively master the principles from the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, learners should follow a structured upskilling path. This begins with understanding core concepts such as data storage, compute resources, and cloud services, followed by hands-on practice with real data sets. The next stage involves applying advanced features like Time Travel and Data Sharing, then integrating Snowflake with business intelligence and AI pipelines, and finally completing capstone projects that simulate real-world data scenarios. This progression, as designed in Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, transforms theoretical knowledge into practical expertise and helps learners gain the confidence to build scalable, secure, and intelligent cloud data architectures for any industry.
- When compared to traditional systems, the advantages of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture are undeniable. Unlike hardware-bound databases, Snowflake is a fully managed cloud platform that scales automatically in seconds. It supports structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data formats, uses a pay-as-you-go model that reduces operational costs, and integrates end-to-end encryption with role-based access controls for security. With a future that is deeply tied to AI, automation, and the global data cloud, Snowflake represents a platform built for longevity and continuous innovation. Professionals who complete Snowflake Training in Hyderabad gain access to an ecosystem that continues to grow in scope and opportunity, aligning perfectly with the emerging trends of big data, machine learning, and cloud intelligence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Overview of Snowflake Architecture stands as the definitive blueprint for modern data engineering—an architecture built for agility, intelligence, and scale. It redefines how data is stored, processed, and analyzed by offering a multi-layered system that is both technically elegant and operationally efficient. From its separation of compute and storage to its support for real-time collaboration and multi-cloud flexibility, Snowflake has revolutionized the way enterprises manage and monetize data. For learners and working professionals, understanding this architecture through Snowflake Training in Hyderabad provides not just a skill, but a career advantage in the rapidly evolving cloud ecosystem. By mastering the concepts, tools, and best practices of the Overview of Snowflake Architecture, individuals gain the expertise to design cost-efficient, secure, and scalable data platforms that power business decisions worldwide. The future of data is cloud-native, intelligent, and limitless—and with Snowflake, that future begins now.
FAQ's
What is the Overview of Snowflake Architecture?
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture refers to the cloud-native design of the Snowflake data warehouse, built on three main layers — storage, compute, and cloud services. It allows organizations to store, process, and analyze massive datasets efficiently while ensuring high performance, scalability, and security without managing any physical infrastructure.
Why is the Overview of Snowflake Architecture important for data professionals?
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture is crucial because it helps professionals understand how Snowflake separates compute and storage to achieve flexibility and speed. This architecture enables better cost control, concurrent access, and simplified data sharing — key advantages for anyone working in data engineering or analytics.
What are the main components of Snowflake Architecture?
The main components of Snowflake Architecture are:
- Database Storage Layer for structured and semi-structured data.
- Compute Layer (Virtual Warehouses) for running queries and analytics.
- Cloud Services Layer for managing metadata, authentication, and optimization.
Together, these components make Snowflake a highly scalable, secure, and zero-maintenance cloud data platform.
How does Snowflake differ from traditional databases?
Unlike traditional databases, the Overview of Snowflake Architecture separates compute from storage, allowing each to scale independently. It supports multi-cloud deployment across AWS, Azure, and GCP, eliminates manual tuning, and offers automatic optimization — making it faster, more elastic, and more cost-efficient.
What are the real-world use cases of Snowflake Architecture?
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture is applied across multiple industries — in finance for fraud analytics, in healthcare for secure data sharing, in retail for Customer 360° insights, in manufacturing for IoT analytics, and in media for real-time ad performance tracking. Each use case benefits from Snowflake’s scalability and built-in security.
What skills can I gain from Snowflake Training in Hyderabad?
Through Snowflake Training in Hyderabad, learners gain hands-on skills in data loading, warehouse management, performance optimization, security configuration, and integration with BI and AI tools. They also learn to apply concepts from the Overview of Snowflake Architecture in real-world enterprise projects.
What are the career opportunities after learning Snowflake?
Professionals trained in Snowflake can pursue roles such as Snowflake Data Engineer, Cloud Data Architect, BI Developer, or Data Analyst. With the growing adoption of Snowflake worldwide, job opportunities in Hyderabad and abroad continue to expand, offering high salaries and long-term career stability.
Why is Snowflake considered the future of data warehousing?
The Overview of Snowflake Architecture shows that Snowflake is built for the future — it supports AI, ML, and automation workflows; handles structured and unstructured data; and operates seamlessly across multiple clouds. Its intelligent architecture makes it a cornerstone for next-generation data analytics and engineering careers.
